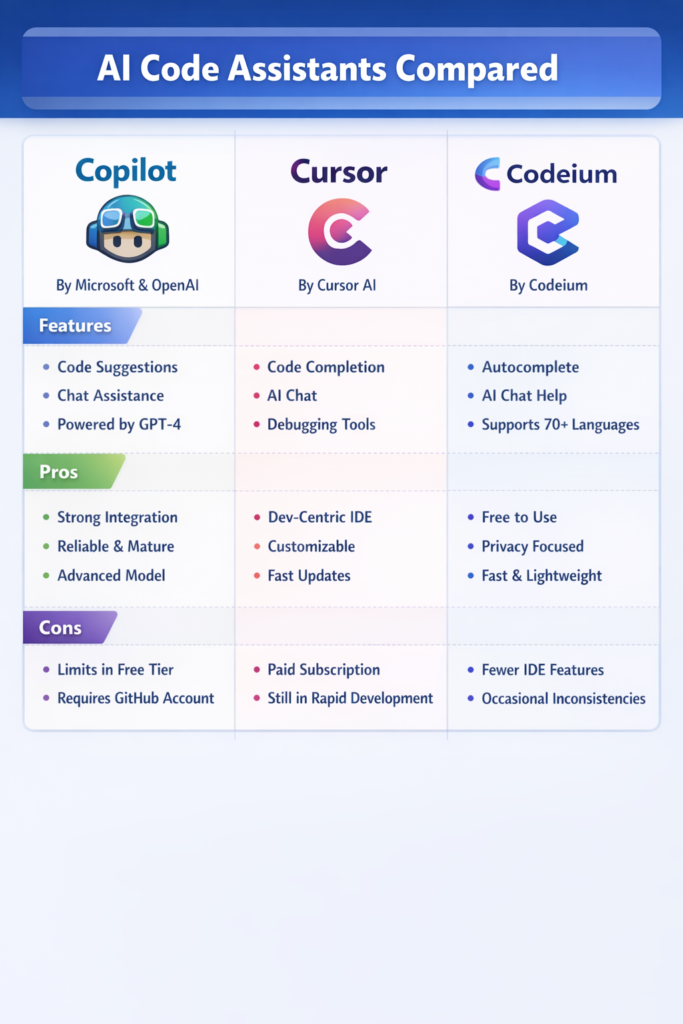
AI code assistants have moved from novelty to daily tooling for many developers. However, not all assistants solve the same problems. This AI code assistants compared guide examines GitHub Copilot, Cursor, and Codeium, three popular tools with different philosophies around productivity, control, and workflow integration.
If you already use AI in your editor but feel uncertain about which tool fits your day-to-day work best, this article helps you make a clearer decision before habits and lock-in form.
What AI Code Assistants Actually Do
At their core, AI code assistants predict code based on context. They analyze your open files, surrounding code, comments, and sometimes repository history to suggest completions or changes.
However, the real difference lies in how they integrate into your workflow. Some tools optimize for inline suggestions. Others focus on conversational editing or refactoring entire files. These distinctions matter more than raw model quality.
If you are already familiar with broader AI tooling in development, many of the same concerns appear in using AI for code refactoring, particularly around trust and review discipline.
GitHub Copilot: Inline Assistance at Scale
GitHub Copilot is the most widely adopted AI code assistant. It integrates directly into popular editors and focuses on inline code completion.
How Copilot Fits Into Daily Work
Copilot works best when you write code incrementally. As you type, it predicts the next few lines based on local context and common patterns across public repositories.
This model works well for boilerplate, repetitive logic, and familiar frameworks. It aligns closely with workflows discussed in integrating GitHub Copilot into your workflow.
Strengths
- Strong inline suggestions
- Excellent editor support
- Minimal workflow disruption
Limitations
- Limited understanding of larger refactors
- Weak at cross-file changes
- Suggestions require careful review
Copilot shines when speed matters more than architectural guidance.
Cursor: Conversational Editing and Deep Context
Cursor takes a different approach. Instead of focusing only on inline suggestions, it treats the editor as a conversational workspace.
How Cursor Changes the Workflow
Cursor allows you to select code, ask questions, and request changes in natural language. As a result, it works well for refactoring, reasoning about logic, and modifying entire files.
This conversational style pairs naturally with patterns described in AI-powered pair programming best practices, where the AI acts more like a collaborator than an autocomplete engine.
Strengths
- Strong at refactoring and explanations
- Handles larger context well
- Encourages deliberate code changes
Limitations
- Slower for quick typing flows
- Requires more explicit prompts
- Best suited for focused sessions
Cursor works best when you want the AI to think with you, not just type for you.
Codeium: Broad Language Support and Accessibility
Codeium positions itself as a free and flexible alternative to paid assistants. It emphasizes wide language support and ease of adoption.
How Codeium Fits Into Teams
Codeium integrates with many editors and supports a large set of languages. Because of this, teams often use it in mixed-language environments or for onboarding developers quickly.
This approach aligns with tooling decisions discussed in top VS Code extensions for full-stack developers, where accessibility and coverage matter.
Strengths
- Free tier with generous limits
- Broad language and IDE support
- Low barrier to entry
Limitations
- Less advanced suggestions in complex code
- Smaller ecosystem
- Fewer deep refactoring features
Codeium is a solid option when cost or language coverage is the primary concern.
Productivity, Accuracy, and Trust
Productivity gains vary by task. Inline completion accelerates repetitive work. Conversational tools help with refactors and understanding unfamiliar code. However, no assistant replaces careful review.
In practice, these tools work best when combined with strong fundamentals, such as those outlined in clean code in Flutter or similar clean-code principles in other ecosystems.
Real-World Scenario: Choosing for a Team
Consider a small product team working on a TypeScript and Flutter codebase. Developers writing UI code benefit from Copilot’s inline speed. Meanwhile, senior engineers use Cursor for refactors and architectural changes. New hires rely on Codeium for quick suggestions across languages.
The takeaway is simple. Teams rarely standardize on a single assistant. Instead, they choose tools based on task type and experience level.
Privacy, Cost, and Policy Considerations
AI assistants process code. As a result, privacy and compliance matter.
- Copilot integrates tightly with GitHub policies
- Cursor focuses on local context and explicit prompts
- Codeium offers flexibility but fewer enterprise controls
These concerns echo broader discussions in ethical considerations using AI tools in coding and should not be ignored.
When to Use GitHub Copilot
Use Copilot if:
- You want fast inline suggestions
- You write a lot of repetitive code
- You value minimal workflow interruption
When to Use Cursor
Cursor is a strong choice when:
- You refactor or reason about code often
- You want conversational editing
- You prefer explicit control over changes
When to Use Codeium
Codeium works best when:
- Cost matters
- Language coverage is important
- You need a simple, accessible assistant
Common Mistakes
- Trusting suggestions without review
- Using AI for logic it does not understand
- Treating assistants as replacements for design
- Ignoring privacy and policy constraints
Conclusion and Next Steps
AI code assistants amplify how you work, not what you know. Copilot excels at speed, Cursor at collaboration, and Codeium at accessibility. Choosing the right tool depends on your workflow, not hype.
As a next step, evaluate which tasks consume most of your time. Then match the assistant to those tasks instead of expecting one tool to solve everything.