Introduction
Since its release by Facebook in 2015, GraphQL has grown into one of the most popular alternatives to REST APIs. In 2025, GraphQL adoption continues to rise as teams seek more efficient, flexible, and developer-friendly ways to expose data.
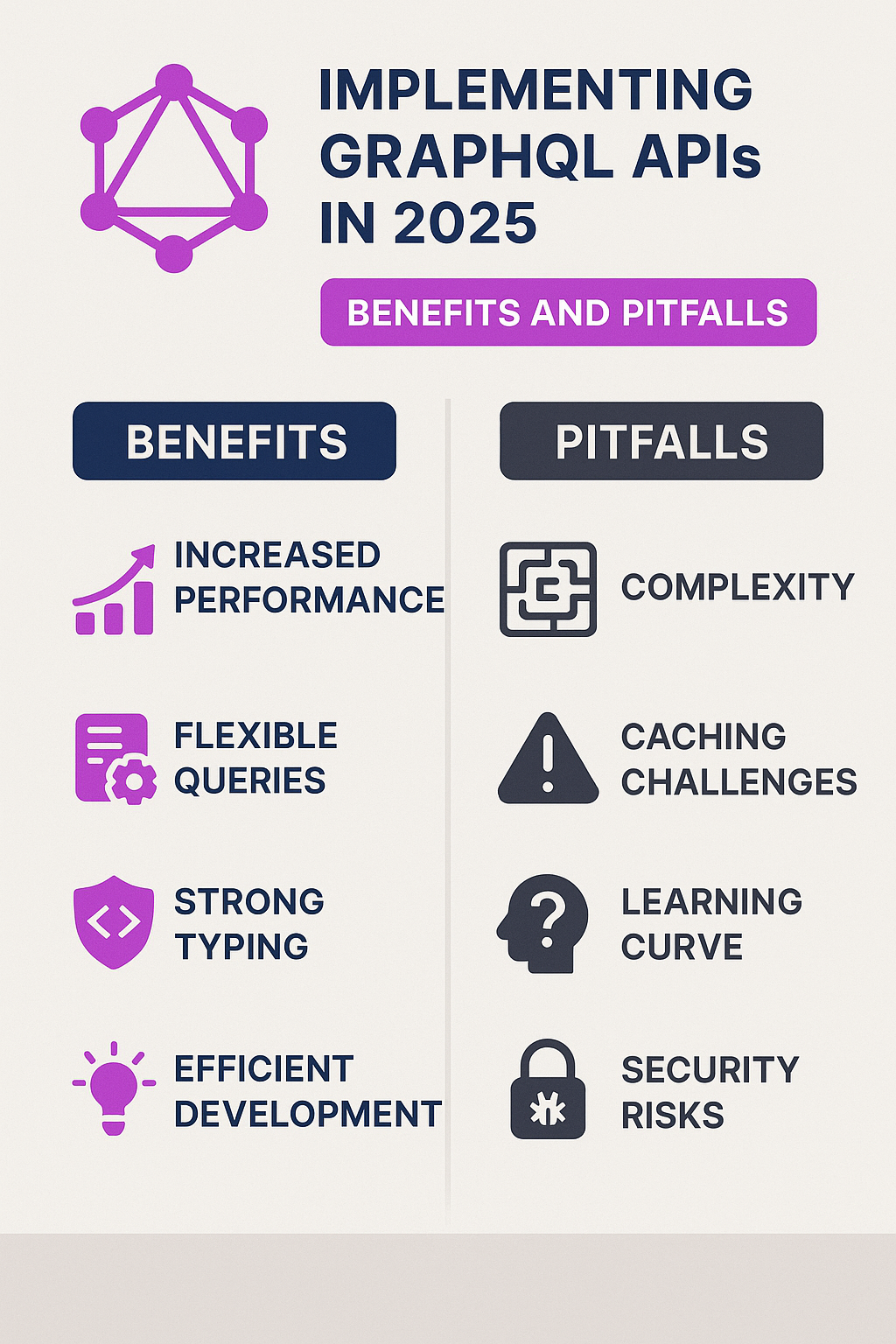
But while GraphQL brings significant benefits, it also comes with challenges that teams must address early on. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the benefits and pitfalls of implementing GraphQL APIs in 2025, complete with practical code examples and production-ready patterns.
Benefits of GraphQL APIs
1. Flexible Data Fetching
Clients can request exactly the fields they need – no more under-fetching or over-fetching. This makes GraphQL perfect for modern frontend frameworks.
# Client can request only what's needed
query GetUserProfile {
user(id: "123") {
name
email
# Don't need address? Don't request it!
}
}
# Different view needs different data
query GetUserWithOrders {
user(id: "123") {
name
orders(first: 5) {
id
total
status
}
}
}2. Strongly Typed Schema
The schema acts as a contract between client and server. It improves collaboration, enables auto-generated documentation, and makes integration less error-prone.
3. Single Endpoint
Unlike REST, where multiple endpoints are required, GraphQL exposes a single endpoint that handles all queries and mutations. This simplifies versioning and reduces complexity.
4. Rich Developer Tooling
Tools like GraphQL Playground and Apollo Studio allow developers to explore queries, test APIs, and monitor performance in real time.
Complete GraphQL Server Implementation
Let’s build a production-ready GraphQL API using Apollo Server v4 with TypeScript.
Schema Definition
# schema.graphql
type Query {
user(id: ID!): User
users(filter: UserFilter, pagination: PaginationInput): UserConnection!
product(id: ID!): Product
products(filter: ProductFilter, pagination: PaginationInput): ProductConnection!
}
type Mutation {
createUser(input: CreateUserInput!): User!
updateUser(id: ID!, input: UpdateUserInput!): User!
deleteUser(id: ID!): Boolean!
createOrder(input: CreateOrderInput!): Order!
}
type Subscription {
orderStatusChanged(userId: ID!): Order!
newNotification(userId: ID!): Notification!
}
type User {
id: ID!
email: String!
name: String!
role: UserRole!
orders(first: Int, after: String): OrderConnection!
createdAt: DateTime!
updatedAt: DateTime!
}
type Product {
id: ID!
name: String!
description: String
price: Float!
inventory: Int!
category: Category!
reviews(first: Int): [Review!]!
}
type Order {
id: ID!
user: User!
items: [OrderItem!]!
status: OrderStatus!
total: Float!
createdAt: DateTime!
}
type OrderItem {
product: Product!
quantity: Int!
price: Float!
}
type Review {
id: ID!
user: User!
rating: Int!
comment: String
createdAt: DateTime!
}
type Category {
id: ID!
name: String!
products(first: Int): [Product!]!
}
enum UserRole {
USER
ADMIN
MODERATOR
}
enum OrderStatus {
PENDING
PROCESSING
SHIPPED
DELIVERED
CANCELLED
}
# Connection types for pagination
type UserConnection {
edges: [UserEdge!]!
pageInfo: PageInfo!
totalCount: Int!
}
type UserEdge {
node: User!
cursor: String!
}
type OrderConnection {
edges: [OrderEdge!]!
pageInfo: PageInfo!
totalCount: Int!
}
type OrderEdge {
node: Order!
cursor: String!
}
type ProductConnection {
edges: [ProductEdge!]!
pageInfo: PageInfo!
totalCount: Int!
}
type ProductEdge {
node: Product!
cursor: String!
}
type PageInfo {
hasNextPage: Boolean!
hasPreviousPage: Boolean!
startCursor: String
endCursor: String
}
type Notification {
id: ID!
type: NotificationType!
message: String!
read: Boolean!
createdAt: DateTime!
}
enum NotificationType {
ORDER_UPDATE
PROMOTION
SYSTEM
}
input CreateUserInput {
email: String!
name: String!
password: String!
}
input UpdateUserInput {
email: String
name: String
}
input CreateOrderInput {
items: [OrderItemInput!]!
}
input OrderItemInput {
productId: ID!
quantity: Int!
}
input UserFilter {
role: UserRole
search: String
}
input ProductFilter {
categoryId: ID
minPrice: Float
maxPrice: Float
search: String
}
input PaginationInput {
first: Int
after: String
last: Int
before: String
}
scalar DateTimeServer Setup with Apollo Server v4
// src/index.ts
import { ApolloServer } from '@apollo/server';
import { expressMiddleware } from '@apollo/server/express4';
import { ApolloServerPluginDrainHttpServer } from '@apollo/server/plugin/drainHttpServer';
import { makeExecutableSchema } from '@graphql-tools/schema';
import { WebSocketServer } from 'ws';
import { useServer } from 'graphql-ws/lib/use/ws';
import express from 'express';
import http from 'http';
import cors from 'cors';
import { typeDefs } from './schema';
import { resolvers } from './resolvers';
import { createContext, Context } from './context';
import { authPlugin } from './plugins/auth';
import { complexityPlugin } from './plugins/complexity';
import { loggingPlugin } from './plugins/logging';
async function startServer() {
const app = express();
const httpServer = http.createServer(app);
const schema = makeExecutableSchema({ typeDefs, resolvers });
// WebSocket server for subscriptions
const wsServer = new WebSocketServer({
server: httpServer,
path: '/graphql',
});
const serverCleanup = useServer(
{
schema,
context: async (ctx) => {
// Authenticate WebSocket connections
const token = ctx.connectionParams?.authorization;
return createContext({ token });
},
},
wsServer
);
const server = new ApolloServer<Context>({
schema,
plugins: [
// Proper shutdown for HTTP server
ApolloServerPluginDrainHttpServer({ httpServer }),
// Proper shutdown for WebSocket server
{
async serverWillStart() {
return {
async drainServer() {
await serverCleanup.dispose();
},
};
},
},
authPlugin,
complexityPlugin,
loggingPlugin,
],
formatError: (formattedError, error) => {
// Don't expose internal errors to clients
if (process.env.NODE_ENV === 'production') {
if (formattedError.extensions?.code === 'INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR') {
return {
message: 'Internal server error',
extensions: { code: 'INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR' },
};
}
}
return formattedError;
},
});
await server.start();
app.use(
'/graphql',
cors<cors.CorsRequest>(),
express.json(),
expressMiddleware(server, {
context: async ({ req }) => createContext({ req }),
})
);
const PORT = process.env.PORT || 4000;
httpServer.listen(PORT, () => {
console.log(`Server ready at http://localhost:${PORT}/graphql`);
console.log(`Subscriptions ready at ws://localhost:${PORT}/graphql`);
});
}
startServer();Context and Authentication
// src/context.ts
import { Request } from 'express';
import { PrismaClient } from '@prisma/client';
import DataLoader from 'dataloader';
import { verifyToken } from './auth';
import { createLoaders, Loaders } from './loaders';
const prisma = new PrismaClient();
export interface Context {
prisma: PrismaClient;
user: { id: string; role: string } | null;
loaders: Loaders;
}
interface CreateContextParams {
req?: Request;
token?: string;
}
export async function createContext({ req, token }: CreateContextParams): Promise<Context> {
// Get token from header or direct param (for WebSocket)
const authToken = token || req?.headers.authorization?.replace('Bearer ', '');
let user = null;
if (authToken) {
try {
user = await verifyToken(authToken);
} catch (error) {
// Invalid token, user stays null
}
}
return {
prisma,
user,
loaders: createLoaders(prisma),
};
}DataLoader for N+1 Prevention
// src/loaders.ts
import DataLoader from 'dataloader';
import { PrismaClient } from '@prisma/client';
export interface Loaders {
userLoader: DataLoader<string, any>;
productLoader: DataLoader<string, any>;
categoryLoader: DataLoader<string, any>;
ordersByUserLoader: DataLoader<string, any[]>;
reviewsByProductLoader: DataLoader<string, any[]>;
}
export function createLoaders(prisma: PrismaClient): Loaders {
return {
// Batch load users by ID
userLoader: new DataLoader(async (ids: readonly string[]) => {
const users = await prisma.user.findMany({
where: { id: { in: [...ids] } },
});
const userMap = new Map(users.map((u) => [u.id, u]));
return ids.map((id) => userMap.get(id) || null);
}),
// Batch load products by ID
productLoader: new DataLoader(async (ids: readonly string[]) => {
const products = await prisma.product.findMany({
where: { id: { in: [...ids] } },
});
const productMap = new Map(products.map((p) => [p.id, p]));
return ids.map((id) => productMap.get(id) || null);
}),
// Batch load categories by ID
categoryLoader: new DataLoader(async (ids: readonly string[]) => {
const categories = await prisma.category.findMany({
where: { id: { in: [...ids] } },
});
const categoryMap = new Map(categories.map((c) => [c.id, c]));
return ids.map((id) => categoryMap.get(id) || null);
}),
// Batch load orders by user ID
ordersByUserLoader: new DataLoader(async (userIds: readonly string[]) => {
const orders = await prisma.order.findMany({
where: { userId: { in: [...userIds] } },
orderBy: { createdAt: 'desc' },
});
const ordersMap = new Map<string, any[]>();
orders.forEach((order) => {
const existing = ordersMap.get(order.userId) || [];
existing.push(order);
ordersMap.set(order.userId, existing);
});
return userIds.map((id) => ordersMap.get(id) || []);
}),
// Batch load reviews by product ID
reviewsByProductLoader: new DataLoader(async (productIds: readonly string[]) => {
const reviews = await prisma.review.findMany({
where: { productId: { in: [...productIds] } },
orderBy: { createdAt: 'desc' },
});
const reviewsMap = new Map<string, any[]>();
reviews.forEach((review) => {
const existing = reviewsMap.get(review.productId) || [];
existing.push(review);
reviewsMap.set(review.productId, existing);
});
return productIds.map((id) => reviewsMap.get(id) || []);
}),
};
}Resolvers with DataLoader
// src/resolvers/index.ts
import { GraphQLDateTime } from 'graphql-scalars';
import { userResolvers } from './user';
import { productResolvers } from './product';
import { orderResolvers } from './order';
export const resolvers = {
DateTime: GraphQLDateTime,
...userResolvers,
...productResolvers,
...orderResolvers,
};
// src/resolvers/user.ts
import { GraphQLError } from 'graphql';
import { Context } from '../context';
import { encodeCursor, decodeCursor } from '../utils/pagination';
export const userResolvers = {
Query: {
user: async (_: any, { id }: { id: string }, { loaders }: Context) => {
return loaders.userLoader.load(id);
},
users: async (
_: any,
{ filter, pagination }: any,
{ prisma, user }: Context
) => {
// Only admins can list all users
if (!user || user.role !== 'ADMIN') {
throw new GraphQLError('Not authorized', {
extensions: { code: 'FORBIDDEN' },
});
}
const { first = 20, after } = pagination || {};
const cursor = after ? decodeCursor(after) : undefined;
const where: any = {};
if (filter?.role) where.role = filter.role;
if (filter?.search) {
where.OR = [
{ name: { contains: filter.search, mode: 'insensitive' } },
{ email: { contains: filter.search, mode: 'insensitive' } },
];
}
const [users, totalCount] = await Promise.all([
prisma.user.findMany({
where,
take: first + 1,
cursor: cursor ? { id: cursor } : undefined,
skip: cursor ? 1 : 0,
orderBy: { createdAt: 'desc' },
}),
prisma.user.count({ where }),
]);
const hasNextPage = users.length > first;
const edges = users.slice(0, first).map((user) => ({
node: user,
cursor: encodeCursor(user.id),
}));
return {
edges,
pageInfo: {
hasNextPage,
hasPreviousPage: !!cursor,
startCursor: edges[0]?.cursor,
endCursor: edges[edges.length - 1]?.cursor,
},
totalCount,
};
},
},
Mutation: {
createUser: async (_: any, { input }: any, { prisma }: Context) => {
const { email, name, password } = input;
// Check if user exists
const existing = await prisma.user.findUnique({ where: { email } });
if (existing) {
throw new GraphQLError('Email already in use', {
extensions: { code: 'BAD_USER_INPUT' },
});
}
// Hash password (use bcrypt in production)
const hashedPassword = await hashPassword(password);
return prisma.user.create({
data: {
email,
name,
password: hashedPassword,
role: 'USER',
},
});
},
},
User: {
// Resolve user's orders using DataLoader
orders: async (
parent: any,
{ first = 10, after }: any,
{ loaders }: Context
) => {
const allOrders = await loaders.ordersByUserLoader.load(parent.id);
const cursor = after ? decodeCursor(after) : null;
let startIndex = 0;
if (cursor) {
const cursorIndex = allOrders.findIndex((o) => o.id === cursor);
startIndex = cursorIndex + 1;
}
const orders = allOrders.slice(startIndex, startIndex + first + 1);
const hasNextPage = orders.length > first;
const edges = orders.slice(0, first).map((order) => ({
node: order,
cursor: encodeCursor(order.id),
}));
return {
edges,
pageInfo: {
hasNextPage,
hasPreviousPage: startIndex > 0,
startCursor: edges[0]?.cursor,
endCursor: edges[edges.length - 1]?.cursor,
},
totalCount: allOrders.length,
};
},
},
};Security: Query Complexity Limiting
Prevent DoS attacks by limiting query complexity:
// src/plugins/complexity.ts
import {
getComplexity,
simpleEstimator,
fieldExtensionsEstimator,
} from 'graphql-query-complexity';
import { GraphQLError } from 'graphql';
const MAX_COMPLEXITY = 1000;
export const complexityPlugin = {
async requestDidStart() {
return {
async didResolveOperation({ request, document, schema }: any) {
const complexity = getComplexity({
schema,
operationName: request.operationName,
query: document,
variables: request.variables,
estimators: [
fieldExtensionsEstimator(),
simpleEstimator({ defaultComplexity: 1 }),
],
});
if (complexity > MAX_COMPLEXITY) {
throw new GraphQLError(
`Query too complex: ${complexity}. Maximum allowed: ${MAX_COMPLEXITY}`,
{
extensions: { code: 'QUERY_TOO_COMPLEX' },
}
);
}
console.log(`Query complexity: ${complexity}`);
},
};
},
};Real-Time Subscriptions
// src/resolvers/subscription.ts
import { PubSub } from 'graphql-subscriptions';
import { Context } from '../context';
const pubsub = new PubSub();
export const ORDER_STATUS_CHANGED = 'ORDER_STATUS_CHANGED';
export const NEW_NOTIFICATION = 'NEW_NOTIFICATION';
export const subscriptionResolvers = {
Subscription: {
orderStatusChanged: {
subscribe: (_: any, { userId }: { userId: string }, { user }: Context) => {
// Ensure user can only subscribe to their own orders
if (!user || (user.id !== userId && user.role !== 'ADMIN')) {
throw new Error('Not authorized');
}
return pubsub.asyncIterator([`${ORDER_STATUS_CHANGED}:${userId}`]);
},
},
newNotification: {
subscribe: (_: any, { userId }: { userId: string }, { user }: Context) => {
if (!user || user.id !== userId) {
throw new Error('Not authorized');
}
return pubsub.asyncIterator([`${NEW_NOTIFICATION}:${userId}`]);
},
},
},
};
// Publishing events (call from your business logic)
export function publishOrderStatusChange(userId: string, order: any) {
pubsub.publish(`${ORDER_STATUS_CHANGED}:${userId}`, {
orderStatusChanged: order,
});
}
export function publishNotification(userId: string, notification: any) {
pubsub.publish(`${NEW_NOTIFICATION}:${userId}`, {
newNotification: notification,
});
}Client-Side Usage with Apollo Client
// React/Next.js client setup
import { ApolloClient, InMemoryCache, ApolloProvider, split, HttpLink } from '@apollo/client';
import { GraphQLWsLink } from '@apollo/client/link/subscriptions';
import { createClient } from 'graphql-ws';
import { getMainDefinition } from '@apollo/client/utilities';
const httpLink = new HttpLink({
uri: 'http://localhost:4000/graphql',
headers: {
authorization: `Bearer ${getToken()}`,
},
});
const wsLink = new GraphQLWsLink(
createClient({
url: 'ws://localhost:4000/graphql',
connectionParams: {
authorization: getToken(),
},
})
);
const splitLink = split(
({ query }) => {
const definition = getMainDefinition(query);
return (
definition.kind === 'OperationDefinition' &&
definition.operation === 'subscription'
);
},
wsLink,
httpLink
);
const client = new ApolloClient({
link: splitLink,
cache: new InMemoryCache({
typePolicies: {
Query: {
fields: {
users: {
keyArgs: ['filter'],
merge(existing, incoming, { args }) {
if (!args?.pagination?.after) {
return incoming;
}
return {
...incoming,
edges: [...(existing?.edges || []), ...incoming.edges],
};
},
},
},
},
},
}),
});
// Usage in components
import { useQuery, useSubscription } from '@apollo/client';
import { gql } from '@apollo/client';
const GET_USERS = gql`
query GetUsers($filter: UserFilter, $pagination: PaginationInput) {
users(filter: $filter, pagination: $pagination) {
edges {
node {
id
name
email
role
}
cursor
}
pageInfo {
hasNextPage
endCursor
}
totalCount
}
}
`;
function UserList() {
const { data, loading, fetchMore } = useQuery(GET_USERS, {
variables: { pagination: { first: 20 } },
});
const loadMore = () => {
fetchMore({
variables: {
pagination: {
first: 20,
after: data.users.pageInfo.endCursor,
},
},
});
};
// Render users...
}Common Mistakes to Avoid
1. Not using DataLoader
// Wrong: N+1 problem - each order triggers a user query
Order: {
user: async (parent, _, { prisma }) => {
return prisma.user.findUnique({ where: { id: parent.userId } });
}
}
// Correct: Batch with DataLoader
Order: {
user: async (parent, _, { loaders }) => {
return loaders.userLoader.load(parent.userId);
}
}2. Exposing sensitive data without authorization
// Wrong: Anyone can query any user's data
user: async (_, { id }, { prisma }) => prisma.user.findUnique({ where: { id } })
// Correct: Check authorization
user: async (_, { id }, { prisma, user }) => {
if (!user || (user.id !== id && user.role !== 'ADMIN')) {
throw new GraphQLError('Not authorized');
}
return prisma.user.findUnique({ where: { id } });
}3. No query depth or complexity limits
# Malicious query without limits can crash your server
query DeepQuery {
user(id: "1") {
orders {
edges {
node {
user {
orders {
edges {
node {
user {
# ... infinite depth
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}4. Not handling errors properly
// Wrong: Generic errors expose internals
throw new Error('Database connection failed: postgres://user:pass@host/db');
// Correct: User-friendly errors with codes
throw new GraphQLError('Unable to process request', {
extensions: { code: 'INTERNAL_ERROR' },
});When to Use GraphQL vs REST
| Use Case | Best Choice |
|---|---|
| Multiple frontend clients with different data needs | GraphQL |
| Simple CRUD API | REST |
| Complex nested data | GraphQL |
| File uploads | REST |
| Real-time subscriptions | GraphQL |
| High caching requirements | REST |
| Rapid frontend iteration | GraphQL |
Related
- gRPC vs REST in 2025
- API Rate Limiting 101: Protect Your Backend from Abuse
- Deploying Spring Boot Apps to Docker and Kubernetes
Conclusion
Implementing GraphQL APIs in 2025 offers flexibility, strong typing, and excellent developer experience. But teams must carefully address performance (DataLoader), security (complexity limits, authorization), and caching challenges.
For projects with complex data relationships and multiple frontend clients, GraphQL is often the right choice. For simpler applications or those with heavy caching requirements, REST or a hybrid approach may be more pragmatic. The key is understanding both options and choosing based on your specific requirements.