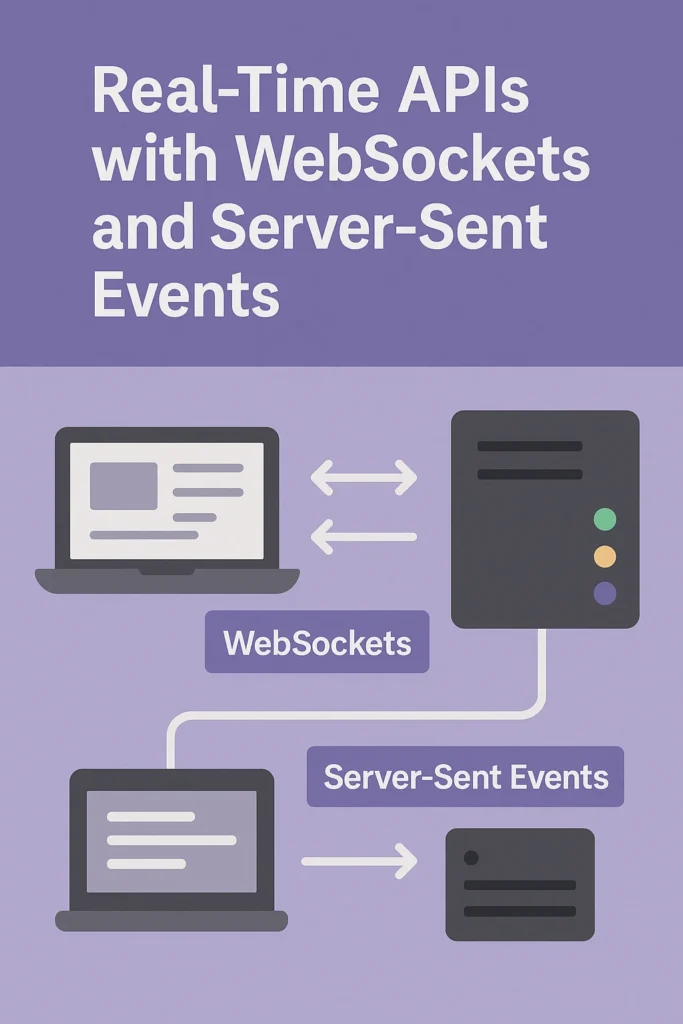
Why Real-Time APIs Matter
Modern applications demand instant feedback. Whether it’s a chat message appearing immediately, a stock price updating live, or a collaborative document syncing across users, people expect updates without refreshing the page. This expectation has fundamentally changed how we architect web applications.
Traditional REST APIs use a request-response model—the client asks, the server answers. This works perfectly for fetching resources or submitting forms, but falls short when the server needs to push updates to clients. Repeated polling wastes bandwidth, increases latency, and creates unnecessary server load.
That’s why technologies like WebSockets and Server-Sent Events (SSE) are essential for building responsive, real-time experiences. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore both technologies, implement complete examples, and help you choose the right approach for your use case.
The Evolution from Polling to Real-Time
Before diving into WebSockets and SSE, let’s understand the progression of real-time techniques:
// 1. Short Polling - Simple but inefficient
setInterval(async () => {
const response = await fetch('/api/messages');
const messages = await response.json();
updateUI(messages);
}, 3000); // Check every 3 seconds
// Problems:
// - Wasted requests when nothing changed
// - 3-second minimum delay for new messages
// - Server processes many empty responses
// 2. Long Polling - Better but still has overhead
async function longPoll() {
try {
const response = await fetch('/api/messages/poll', {
timeout: 30000 // Server holds request up to 30s
});
const messages = await response.json();
updateUI(messages);
} finally {
longPoll(); // Immediately reconnect
}
}
// Problems:
// - HTTP overhead for each reconnection
// - Connection timeouts and proxy issues
// - Complex error handling
// 3. WebSockets - True bidirectional
const ws = new WebSocket('wss://api.example.com/ws');
ws.onmessage = (event) => updateUI(JSON.parse(event.data));
ws.send(JSON.stringify({ type: 'subscribe', channel: 'messages' }));
// Benefits:
// - Single persistent connection
// - Sub-millisecond latency
// - Full duplex communicationWebSockets: Full-Duplex Communication
WebSockets provide a persistent, bidirectional communication channel between client and server. After an initial HTTP handshake, the connection upgrades to the WebSocket protocol, allowing both sides to send messages at any time without the overhead of HTTP headers.
Complete WebSocket Server Implementation
// server/websocket-server.js
const WebSocket = require('ws');
const http = require('http');
const jwt = require('jsonwebtoken');
const { v4: uuidv4 } = require('uuid');
class ChatServer {
constructor(server) {
this.wss = new WebSocket.Server({ server });
this.clients = new Map(); // clientId -> { socket, user, rooms }
this.rooms = new Map(); // roomId -> Set of clientIds
this.wss.on('connection', (socket, request) => {
this.handleConnection(socket, request);
});
// Heartbeat to detect dead connections
this.startHeartbeat();
}
handleConnection(socket, request) {
const clientId = uuidv4();
// Extract token from query string
const url = new URL(request.url, 'http://localhost');
const token = url.searchParams.get('token');
try {
const user = jwt.verify(token, process.env.JWT_SECRET);
this.clients.set(clientId, {
socket,
user,
rooms: new Set(),
isAlive: true
});
socket.clientId = clientId;
this.send(socket, {
type: 'connected',
clientId,
user: { id: user.id, name: user.name }
});
socket.on('message', (data) => this.handleMessage(clientId, data));
socket.on('close', () => this.handleDisconnect(clientId));
socket.on('pong', () => {
const client = this.clients.get(clientId);
if (client) client.isAlive = true;
});
} catch (error) {
socket.close(4001, 'Unauthorized');
}
}
handleMessage(clientId, data) {
const client = this.clients.get(clientId);
if (!client) return;
try {
const message = JSON.parse(data);
switch (message.type) {
case 'join-room':
this.joinRoom(clientId, message.roomId);
break;
case 'leave-room':
this.leaveRoom(clientId, message.roomId);
break;
case 'chat-message':
this.broadcastToRoom(message.roomId, {
type: 'chat-message',
roomId: message.roomId,
senderId: client.user.id,
senderName: client.user.name,
content: message.content,
timestamp: Date.now()
}, clientId);
break;
case 'typing':
this.broadcastToRoom(message.roomId, {
type: 'typing',
userId: client.user.id,
userName: client.user.name,
isTyping: message.isTyping
}, clientId);
break;
default:
this.send(client.socket, { type: 'error', message: 'Unknown message type' });
}
} catch (error) {
console.error('Message parse error:', error);
}
}
joinRoom(clientId, roomId) {
const client = this.clients.get(clientId);
if (!client) return;
if (!this.rooms.has(roomId)) {
this.rooms.set(roomId, new Set());
}
this.rooms.get(roomId).add(clientId);
client.rooms.add(roomId);
this.send(client.socket, {
type: 'room-joined',
roomId,
members: this.getRoomMembers(roomId)
});
this.broadcastToRoom(roomId, {
type: 'user-joined',
userId: client.user.id,
userName: client.user.name
}, clientId);
}
leaveRoom(clientId, roomId) {
const client = this.clients.get(clientId);
if (!client) return;
const room = this.rooms.get(roomId);
if (room) {
room.delete(clientId);
client.rooms.delete(roomId);
this.broadcastToRoom(roomId, {
type: 'user-left',
userId: client.user.id,
userName: client.user.name
});
if (room.size === 0) {
this.rooms.delete(roomId);
}
}
}
handleDisconnect(clientId) {
const client = this.clients.get(clientId);
if (!client) return;
// Leave all rooms
for (const roomId of client.rooms) {
this.leaveRoom(clientId, roomId);
}
this.clients.delete(clientId);
}
broadcastToRoom(roomId, message, excludeClientId = null) {
const room = this.rooms.get(roomId);
if (!room) return;
for (const clientId of room) {
if (clientId === excludeClientId) continue;
const client = this.clients.get(clientId);
if (client) {
this.send(client.socket, message);
}
}
}
getRoomMembers(roomId) {
const room = this.rooms.get(roomId);
if (!room) return [];
return Array.from(room).map(clientId => {
const client = this.clients.get(clientId);
return client ? { id: client.user.id, name: client.user.name } : null;
}).filter(Boolean);
}
send(socket, data) {
if (socket.readyState === WebSocket.OPEN) {
socket.send(JSON.stringify(data));
}
}
startHeartbeat() {
setInterval(() => {
for (const [clientId, client] of this.clients) {
if (!client.isAlive) {
client.socket.terminate();
this.handleDisconnect(clientId);
continue;
}
client.isAlive = false;
client.socket.ping();
}
}, 30000);
}
}
// Start server
const server = http.createServer();
const chatServer = new ChatServer(server);
server.listen(8080, () => console.log('WebSocket server running on :8080'));React WebSocket Client
// hooks/useWebSocket.ts
import { useEffect, useRef, useState, useCallback } from 'react';
interface WebSocketOptions {
url: string;
token: string;
onMessage?: (message: any) => void;
onConnect?: () => void;
onDisconnect?: () => void;
reconnectAttempts?: number;
reconnectInterval?: number;
}
export function useWebSocket(options: WebSocketOptions) {
const {
url,
token,
onMessage,
onConnect,
onDisconnect,
reconnectAttempts = 5,
reconnectInterval = 3000
} = options;
const wsRef = useRef<WebSocket | null>(null);
const reconnectCountRef = useRef(0);
const [isConnected, setIsConnected] = useState(false);
const [connectionError, setConnectionError] = useState<string | null>(null);
const connect = useCallback(() => {
const wsUrl = `${url}?token=${encodeURIComponent(token)}`;
const ws = new WebSocket(wsUrl);
ws.onopen = () => {
setIsConnected(true);
setConnectionError(null);
reconnectCountRef.current = 0;
onConnect?.();
};
ws.onmessage = (event) => {
try {
const message = JSON.parse(event.data);
onMessage?.(message);
} catch (error) {
console.error('Failed to parse message:', error);
}
};
ws.onclose = (event) => {
setIsConnected(false);
wsRef.current = null;
onDisconnect?.();
// Attempt reconnection if not intentionally closed
if (event.code !== 1000 && reconnectCountRef.current < reconnectAttempts) {
reconnectCountRef.current++;
setTimeout(connect, reconnectInterval);
}
};
ws.onerror = () => {
setConnectionError('Connection failed');
};
wsRef.current = ws;
}, [url, token, onMessage, onConnect, onDisconnect, reconnectAttempts, reconnectInterval]);
const disconnect = useCallback(() => {
wsRef.current?.close(1000, 'Client disconnect');
}, []);
const send = useCallback((data: any) => {
if (wsRef.current?.readyState === WebSocket.OPEN) {
wsRef.current.send(JSON.stringify(data));
}
}, []);
useEffect(() => {
connect();
return () => disconnect();
}, [connect, disconnect]);
return { isConnected, connectionError, send, disconnect };
}
// components/ChatRoom.tsx
import { useState, useCallback } from 'react';
import { useWebSocket } from '../hooks/useWebSocket';
interface Message {
senderId: string;
senderName: string;
content: string;
timestamp: number;
}
export function ChatRoom({ roomId, token }: { roomId: string; token: string }) {
const [messages, setMessages] = useState<Message[]>([]);
const [typingUsers, setTypingUsers] = useState<Set<string>>(new Set());
const [inputValue, setInputValue] = useState('');
const handleMessage = useCallback((message: any) => {
switch (message.type) {
case 'chat-message':
setMessages(prev => [...prev, message]);
break;
case 'typing':
setTypingUsers(prev => {
const next = new Set(prev);
if (message.isTyping) {
next.add(message.userName);
} else {
next.delete(message.userName);
}
return next;
});
break;
case 'user-joined':
setMessages(prev => [...prev, {
senderId: 'system',
senderName: 'System',
content: `${message.userName} joined the room`,
timestamp: Date.now()
}]);
break;
}
}, []);
const { isConnected, send } = useWebSocket({
url: 'wss://api.example.com/ws',
token,
onMessage: handleMessage,
onConnect: () => send({ type: 'join-room', roomId })
});
const handleSend = () => {
if (inputValue.trim()) {
send({ type: 'chat-message', roomId, content: inputValue });
setInputValue('');
}
};
const handleTyping = (isTyping: boolean) => {
send({ type: 'typing', roomId, isTyping });
};
return (
<div className="chat-room">
<div className="status">{isConnected ? 'Connected' : 'Disconnected'}</div>
<div className="messages">
{messages.map((msg, i) => (
<div key={i} className="message">
<strong>{msg.senderName}:</strong> {msg.content}
</div>
))}
</div>
{typingUsers.size > 0 && (
<div className="typing">
{Array.from(typingUsers).join(', ')} typing...
</div>
)}
<input
value={inputValue}
onChange={(e) => setInputValue(e.target.value)}
onFocus={() => handleTyping(true)}
onBlur={() => handleTyping(false)}
onKeyPress={(e) => e.key === 'Enter' && handleSend()}
/>
<button onClick={handleSend}>Send</button>
</div>
);
}Server-Sent Events: Efficient One-Way Streaming
Server-Sent Events provide a simpler alternative when you only need server-to-client communication. SSE uses standard HTTP, making it easier to deploy behind load balancers and proxies.
Complete SSE Server Implementation
// server/sse-server.js
const express = require('express');
const cors = require('cors');
const jwt = require('jsonwebtoken');
const app = express();
app.use(cors());
// Store active connections by user
const connections = new Map(); // userId -> Set of response objects
// Middleware to verify auth
const authenticate = (req, res, next) => {
const token = req.headers.authorization?.replace('Bearer ', '');
try {
req.user = jwt.verify(token, process.env.JWT_SECRET);
next();
} catch (error) {
res.status(401).json({ error: 'Unauthorized' });
}
};
// SSE endpoint for live notifications
app.get('/events/notifications', authenticate, (req, res) => {
const userId = req.user.id;
// SSE headers
res.setHeader('Content-Type', 'text/event-stream');
res.setHeader('Cache-Control', 'no-cache');
res.setHeader('Connection', 'keep-alive');
res.setHeader('X-Accel-Buffering', 'no'); // Disable Nginx buffering
// Send initial connection event
res.write(`event: connected\ndata: ${JSON.stringify({ userId })}\n\n`);
// Register connection
if (!connections.has(userId)) {
connections.set(userId, new Set());
}
connections.get(userId).add(res);
// Heartbeat to keep connection alive
const heartbeat = setInterval(() => {
res.write(`: heartbeat\n\n`);
}, 30000);
// Cleanup on disconnect
req.on('close', () => {
clearInterval(heartbeat);
connections.get(userId)?.delete(res);
if (connections.get(userId)?.size === 0) {
connections.delete(userId);
}
});
});
// SSE endpoint for live stock prices
app.get('/events/stocks/:symbol', (req, res) => {
const { symbol } = req.params;
res.setHeader('Content-Type', 'text/event-stream');
res.setHeader('Cache-Control', 'no-cache');
res.setHeader('Connection', 'keep-alive');
// Simulate stock price updates
const sendPrice = () => {
const price = (100 + Math.random() * 10).toFixed(2);
const change = (Math.random() * 2 - 1).toFixed(2);
res.write(`event: price\ndata: ${JSON.stringify({
symbol,
price: parseFloat(price),
change: parseFloat(change),
timestamp: Date.now()
})}\n\n`);
};
// Send initial price
sendPrice();
// Send updates every second
const interval = setInterval(sendPrice, 1000);
req.on('close', () => {
clearInterval(interval);
});
});
// Function to send notification to specific user
function sendNotification(userId, notification) {
const userConnections = connections.get(userId);
if (!userConnections) return;
const data = JSON.stringify(notification);
for (const res of userConnections) {
res.write(`event: notification\ndata: ${data}\n\n`);
}
}
// Example: Send notification when order is completed
app.post('/api/orders/:orderId/complete', authenticate, async (req, res) => {
const { orderId } = req.params;
// Process order completion...
const order = await completeOrder(orderId);
// Send real-time notification
sendNotification(order.userId, {
type: 'order-completed',
orderId,
message: `Your order #${orderId} has been completed!`,
timestamp: Date.now()
});
res.json({ success: true });
});
app.listen(3000, () => console.log('SSE server running on :3000'));React SSE Client
// hooks/useSSE.ts
import { useEffect, useRef, useState, useCallback } from 'react';
interface SSEOptions {
url: string;
token?: string;
onMessage?: (event: string, data: any) => void;
onError?: (error: Event) => void;
}
export function useSSE(options: SSEOptions) {
const { url, token, onMessage, onError } = options;
const eventSourceRef = useRef<EventSource | null>(null);
const [isConnected, setIsConnected] = useState(false);
useEffect(() => {
// Add auth token as query param (SSE doesn't support custom headers)
const eventUrl = token ? `${url}?token=${encodeURIComponent(token)}` : url;
const eventSource = new EventSource(eventUrl);
eventSource.onopen = () => {
setIsConnected(true);
};
eventSource.onerror = (error) => {
setIsConnected(false);
onError?.(error);
};
// Generic message handler
eventSource.onmessage = (event) => {
try {
const data = JSON.parse(event.data);
onMessage?.('message', data);
} catch (e) {
onMessage?.('message', event.data);
}
};
eventSourceRef.current = eventSource;
return () => {
eventSource.close();
};
}, [url, token, onMessage, onError]);
// Subscribe to specific event types
const addEventListener = useCallback((eventType: string, handler: (data: any) => void) => {
const eventSource = eventSourceRef.current;
if (!eventSource) return () => {};
const listener = (event: MessageEvent) => {
try {
handler(JSON.parse(event.data));
} catch (e) {
handler(event.data);
}
};
eventSource.addEventListener(eventType, listener as any);
return () => eventSource.removeEventListener(eventType, listener as any);
}, []);
return { isConnected, addEventListener };
}
// components/StockTicker.tsx
import { useEffect, useState } from 'react';
import { useSSE } from '../hooks/useSSE';
interface StockPrice {
symbol: string;
price: number;
change: number;
timestamp: number;
}
export function StockTicker({ symbol }: { symbol: string }) {
const [price, setPrice] = useState<StockPrice | null>(null);
const [history, setHistory] = useState<StockPrice[]>([]);
const { isConnected, addEventListener } = useSSE({
url: `/api/events/stocks/${symbol}`
});
useEffect(() => {
return addEventListener('price', (data: StockPrice) => {
setPrice(data);
setHistory(prev => [...prev.slice(-50), data]); // Keep last 50 prices
});
}, [addEventListener]);
return (
<div className="stock-ticker">
<div className="status">
{isConnected ? '🟢 Live' : '🔴 Disconnected'}
</div>
{price && (
<div className="price">
<span className="symbol">{price.symbol}</span>
<span className="value">${price.price.toFixed(2)}</span>
<span className={`change ${price.change >= 0 ? 'up' : 'down'}`}>
{price.change >= 0 ? '+' : ''}{price.change}%
</span>
</div>
)}
<div className="chart">
{/* Render price history as a simple sparkline */}
{history.map((p, i) => (
<div
key={i}
className="bar"
style={{ height: `${(p.price - 95) * 10}px` }}
/>
))}
</div>
</div>
);
}
// components/NotificationCenter.tsx
import { useEffect, useState } from 'react';
import { useSSE } from '../hooks/useSSE';
interface Notification {
type: string;
message: string;
timestamp: number;
}
export function NotificationCenter({ token }: { token: string }) {
const [notifications, setNotifications] = useState<Notification[]>([]);
const { isConnected, addEventListener } = useSSE({
url: '/api/events/notifications',
token
});
useEffect(() => {
return addEventListener('notification', (data: Notification) => {
setNotifications(prev => [data, ...prev].slice(0, 50));
// Show browser notification if permitted
if (Notification.permission === 'granted') {
new Notification('New Notification', { body: data.message });
}
});
}, [addEventListener]);
return (
<div className="notification-center">
<h3>Notifications {isConnected && '(Live)'}</h3>
{notifications.map((n, i) => (
<div key={i} className={`notification ${n.type}`}>
{n.message}
<span className="time">
{new Date(n.timestamp).toLocaleTimeString()}
</span>
</div>
))}
</div>
);
}WebSockets vs SSE: Comprehensive Comparison
| Feature | WebSockets | Server-Sent Events |
|---|---|---|
| Direction | Bidirectional (full-duplex) | Unidirectional (server → client) |
| Protocol | WebSocket (ws:// or wss://) | HTTP/HTTPS |
| Reconnection | Manual implementation | Automatic with EventSource |
| Binary data | Supported | Text only (base64 for binary) |
| Headers | Custom headers on upgrade | No custom headers (use query params) |
| Proxy support | May require configuration | Works out of the box |
| Max connections | Limited by OS/server | HTTP/2 multiplexes connections |
| Message types | Custom protocol | Named events with data field |
| Complexity | Higher (connection management) | Lower (uses standard HTTP) |
Scaling Real-Time APIs
Real-time applications face unique scaling challenges because they maintain persistent connections. Here’s how to handle scaling with Redis Pub/Sub:
// Scaling WebSockets with Redis Pub/Sub
const Redis = require('ioredis');
const WebSocket = require('ws');
class ScalableWebSocketServer {
constructor(server) {
this.wss = new WebSocket.Server({ server });
this.localClients = new Map();
// Redis for cross-server communication
this.publisher = new Redis(process.env.REDIS_URL);
this.subscriber = new Redis(process.env.REDIS_URL);
// Subscribe to broadcast channel
this.subscriber.subscribe('broadcast', 'room:*');
this.subscriber.on('message', (channel, message) => {
this.handleRedisMessage(channel, JSON.parse(message));
});
this.wss.on('connection', this.handleConnection.bind(this));
}
handleConnection(socket) {
const clientId = generateId();
this.localClients.set(clientId, { socket, rooms: new Set() });
socket.on('message', (data) => {
const message = JSON.parse(data);
if (message.type === 'broadcast') {
// Publish to Redis so all servers receive it
this.publisher.publish('broadcast', JSON.stringify({
excludeClient: clientId,
...message
}));
} else if (message.type === 'room-message') {
// Publish to room-specific channel
this.publisher.publish(`room:${message.roomId}`, JSON.stringify({
excludeClient: clientId,
...message
}));
}
});
socket.on('close', () => {
this.localClients.delete(clientId);
});
}
handleRedisMessage(channel, message) {
if (channel === 'broadcast') {
// Send to all local clients except sender
for (const [clientId, client] of this.localClients) {
if (clientId !== message.excludeClient) {
this.send(client.socket, message);
}
}
} else if (channel.startsWith('room:')) {
const roomId = channel.replace('room:', '');
// Send to local clients in this room
for (const [clientId, client] of this.localClients) {
if (client.rooms.has(roomId) && clientId !== message.excludeClient) {
this.send(client.socket, message);
}
}
}
}
send(socket, data) {
if (socket.readyState === WebSocket.OPEN) {
socket.send(JSON.stringify(data));
}
}
}When to Use Each Technology
| Use Case | Recommended | Reason |
|---|---|---|
| Chat applications | WebSockets | Bidirectional messaging required |
| Live sports scores | SSE | One-way updates, simple scaling |
| Multiplayer games | WebSockets | Low latency, binary data support |
| Stock tickers | SSE | Server pushes updates, auto-reconnect |
| Collaborative editing | WebSockets | Cursor positions, real-time sync |
| Notification feeds | SSE | Simple updates, good proxy support |
| IoT dashboards | Either | SSE for monitoring, WS for control |
| Video streaming | Neither | Use WebRTC or HLS instead |
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- No heartbeat mechanism: Connections can silently die; implement ping/pong for WebSockets
- Ignoring reconnection: SSE handles this automatically, but WebSocket clients need manual reconnection logic
- Missing authentication: Validate tokens on connection, not just initial handshake
- Unbounded message queues: Slow clients can cause memory issues; implement back-pressure
- No connection limits: Limit connections per user to prevent resource exhaustion
- Forgetting CORS: SSE requires proper CORS headers; WebSockets need origin validation
- Not handling proxy timeouts: Many proxies timeout idle connections; send periodic heartbeats
Conclusion
Real-time APIs transform static applications into dynamic, engaging experiences. The choice between WebSockets and Server-Sent Events depends on your specific requirements:
- Use WebSockets for bidirectional communication, games, and collaborative applications
- Use SSE for server-push notifications, live feeds, and scenarios where simplicity matters
- Combine both when different parts of your application have different needs
For more on building scalable event-driven systems, read our guide on Designing Event-Driven Microservices with Kafka. For official documentation, see MDN’s WebSocket guide and the HTML Living Standard for SSE.


2 Comments