Introduction
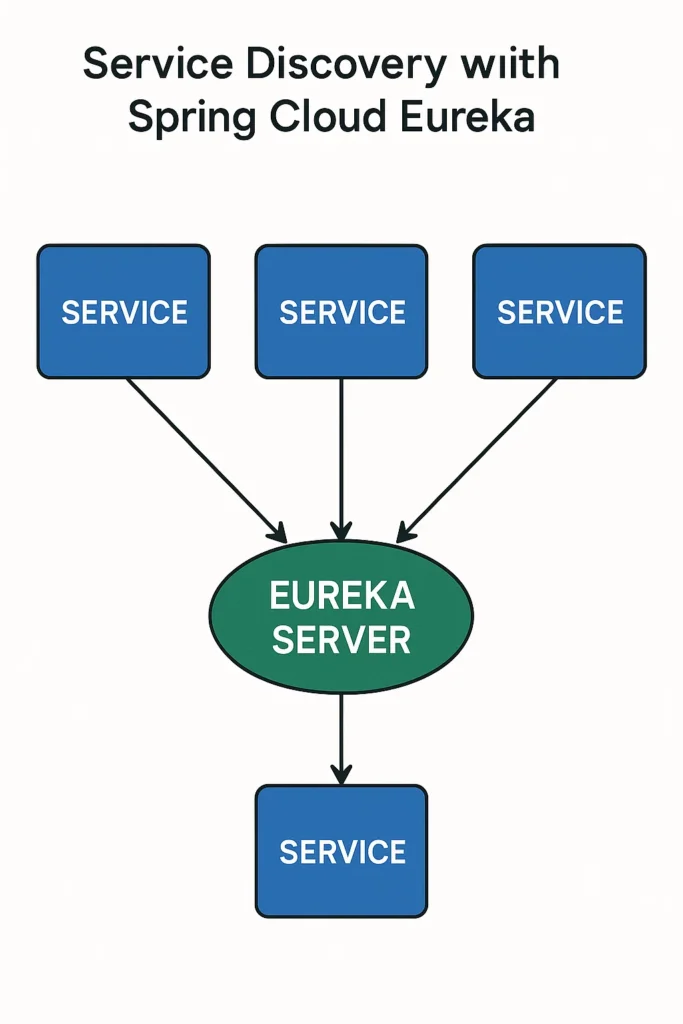
As microservices grow in number, keeping track of service locations becomes a significant challenge. Hardcoding URLs is fragile, especially when services scale, restart, or move to new instances. That’s why service discovery is essential in distributed systems. With Spring Cloud Eureka, services can register themselves automatically and discover each other without manual configuration. In this comprehensive guide, you’ll learn how Eureka works, how to set up a highly available Eureka cluster, implement client-side load balancing, and integrate with Spring Cloud Gateway for production-ready microservices.
What Is Service Discovery?
Service discovery enables services to find each other automatically without hardcoded addresses. Instead of relying on fixed IP addresses or environment variables, services query a registry to locate available instances.
Why It Matters
- Dynamic scaling – Services scale up or down based on demand
- Ephemeral infrastructure – Container IPs change constantly
- Load balancing – Distribute traffic across healthy instances
- Fault tolerance – Route around failed instances automatically
- Zero downtime deployments – New versions register while old ones deregister
Eureka Architecture
Spring Cloud Eureka follows a client-server architecture:
- Eureka Server – Central registry storing all service instances
- Eureka Client – Applications that register with and query the server
- Heartbeats – Periodic signals confirming service health
- Registry cache – Local cache on clients for resilience
Setting Up Eureka Server
Create a Spring Boot project for the Eureka Server:
<!-- pom.xml -->
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>3.2.3</version>
</parent>
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>2023.0.0</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-server</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>Eureka Server Application
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableEurekaServer
public class EurekaServerApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(EurekaServerApplication.class, args);
}
}Standalone Configuration
# application.yml
server:
port: 8761
spring:
application:
name: eureka-server
eureka:
instance:
hostname: localhost
client:
register-with-eureka: false
fetch-registry: false
service-url:
defaultZone: http://localhost:8761/eureka/
server:
enable-self-preservation: true
eviction-interval-timer-in-ms: 60000
response-cache-update-interval-ms: 30000Securing Eureka Server
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
public class SecurityConfig {
@Bean
public SecurityFilterChain filterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
.csrf(csrf -> csrf.ignoringRequestMatchers("/eureka/**"))
.authorizeHttpRequests(auth -> auth
.requestMatchers("/actuator/health").permitAll()
.anyRequest().authenticated()
)
.httpBasic(Customizer.withDefaults());
return http.build();
}
@Bean
public InMemoryUserDetailsManager userDetailsService() {
UserDetails admin = User.withDefaultPasswordEncoder()
.username("eureka")
.password("secret")
.roles("ADMIN")
.build();
return new InMemoryUserDetailsManager(admin);
}
}High Availability Eureka Cluster
For production, run multiple Eureka servers that replicate with each other:
# eureka-server-1 (application-peer1.yml)
server:
port: 8761
spring:
application:
name: eureka-server
eureka:
instance:
hostname: eureka-1
client:
register-with-eureka: true
fetch-registry: true
service-url:
defaultZone: http://eureka:secret@eureka-2:8762/eureka/,http://eureka:secret@eureka-3:8763/eureka/# eureka-server-2 (application-peer2.yml)
server:
port: 8762
eureka:
instance:
hostname: eureka-2
client:
service-url:
defaultZone: http://eureka:secret@eureka-1:8761/eureka/,http://eureka:secret@eureka-3:8763/eureka/# docker-compose.yml
version: '3.8'
services:
eureka-1:
image: eureka-server:latest
environment:
- SPRING_PROFILES_ACTIVE=peer1
ports:
- "8761:8761"
networks:
- microservices
eureka-2:
image: eureka-server:latest
environment:
- SPRING_PROFILES_ACTIVE=peer2
ports:
- "8762:8762"
networks:
- microservices
eureka-3:
image: eureka-server:latest
environment:
- SPRING_PROFILES_ACTIVE=peer3
ports:
- "8763:8763"
networks:
- microservices
networks:
microservices:
driver: bridgeEureka Client Configuration
Set up microservices to register with Eureka:
<!-- Client dependency -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client</artifactId>
</dependency>User Service Example
@SpringBootApplication
public class UserServiceApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(UserServiceApplication.class, args);
}
}# application.yml
spring:
application:
name: user-service
server:
port: 0 # Random port for multiple instances
eureka:
client:
service-url:
defaultZone: http://eureka:secret@localhost:8761/eureka/
registry-fetch-interval-seconds: 5
instance:
instance-id: ${spring.application.name}:${random.uuid}
prefer-ip-address: true
lease-renewal-interval-in-seconds: 10
lease-expiration-duration-in-seconds: 30
metadata-map:
version: 1.0.0
environment: ${spring.profiles.active:default}Order Service Example
# application.yml
spring:
application:
name: order-service
server:
port: 0
eureka:
client:
service-url:
defaultZone: http://eureka:secret@localhost:8761/eureka/
instance:
instance-id: ${spring.application.name}:${random.uuid}
prefer-ip-address: trueService-to-Service Communication
RestTemplate with Load Balancing
@Configuration
public class RestClientConfig {
@Bean
@LoadBalanced
public RestTemplate restTemplate() {
return new RestTemplate();
}
}
@Service
public class OrderService {
private final RestTemplate restTemplate;
public OrderService(RestTemplate restTemplate) {
this.restTemplate = restTemplate;
}
public UserDTO getUserForOrder(Long userId) {
// Eureka resolves "user-service" to actual instance
return restTemplate.getForObject(
"http://user-service/api/users/{id}",
UserDTO.class,
userId
);
}
public List<ProductDTO> getProductsForOrder(List<Long> productIds) {
return restTemplate.exchange(
"http://product-service/api/products/batch",
HttpMethod.POST,
new HttpEntity<>(productIds),
new ParameterizedTypeReference<List<ProductDTO>>() {}
).getBody();
}
}WebClient with Load Balancing
@Configuration
public class WebClientConfig {
@Bean
@LoadBalanced
public WebClient.Builder webClientBuilder() {
return WebClient.builder();
}
}
@Service
public class InventoryService {
private final WebClient.Builder webClientBuilder;
public InventoryService(WebClient.Builder webClientBuilder) {
this.webClientBuilder = webClientBuilder;
}
public Mono<InventoryStatus> checkInventory(Long productId) {
return webClientBuilder.build()
.get()
.uri("http://inventory-service/api/inventory/{productId}", productId)
.retrieve()
.bodyToMono(InventoryStatus.class)
.timeout(Duration.ofSeconds(3))
.onErrorResume(e -> {
log.error("Inventory check failed: {}", e.getMessage());
return Mono.just(InventoryStatus.unknown());
});
}
public Flux<InventoryStatus> checkBulkInventory(List<Long> productIds) {
return webClientBuilder.build()
.post()
.uri("http://inventory-service/api/inventory/bulk")
.bodyValue(productIds)
.retrieve()
.bodyToFlux(InventoryStatus.class);
}
}OpenFeign Declarative Client
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-openfeign</artifactId>
</dependency>@SpringBootApplication
@EnableFeignClients
public class OrderServiceApplication { }
@FeignClient(name = "user-service", fallback = UserClientFallback.class)
public interface UserClient {
@GetMapping("/api/users/{id}")
UserDTO getUserById(@PathVariable Long id);
@GetMapping("/api/users")
List<UserDTO> getAllUsers();
@PostMapping("/api/users")
UserDTO createUser(@RequestBody CreateUserRequest request);
}
@Component
public class UserClientFallback implements UserClient {
@Override
public UserDTO getUserById(Long id) {
return UserDTO.builder()
.id(id)
.name("Unknown User")
.build();
}
@Override
public List<UserDTO> getAllUsers() {
return Collections.emptyList();
}
@Override
public UserDTO createUser(CreateUserRequest request) {
throw new ServiceUnavailableException("User service unavailable");
}
}Integration with Spring Cloud Gateway
Combine Eureka with Spring Cloud Gateway for dynamic routing:
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-gateway</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies># Gateway application.yml
spring:
application:
name: api-gateway
cloud:
gateway:
discovery:
locator:
enabled: true
lower-case-service-id: true
routes:
- id: user-service
uri: lb://user-service
predicates:
- Path=/api/users/**
filters:
- StripPrefix=0
- name: CircuitBreaker
args:
name: userServiceCB
fallbackUri: forward:/fallback/users
- id: order-service
uri: lb://order-service
predicates:
- Path=/api/orders/**
filters:
- StripPrefix=0
- name: Retry
args:
retries: 3
statuses: SERVICE_UNAVAILABLE
- id: product-service
uri: lb://product-service
predicates:
- Path=/api/products/**
filters:
- StripPrefix=0
eureka:
client:
service-url:
defaultZone: http://eureka:secret@localhost:8761/eureka/Gateway Fallback Controller
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/fallback")
public class FallbackController {
@GetMapping("/users")
public ResponseEntity<Map<String, String>> usersFallback() {
return ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.SERVICE_UNAVAILABLE)
.body(Map.of(
"status", "error",
"message", "User service is temporarily unavailable"
));
}
@GetMapping("/orders")
public ResponseEntity<Map<String, String>> ordersFallback() {
return ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.SERVICE_UNAVAILABLE)
.body(Map.of(
"status", "error",
"message", "Order service is temporarily unavailable"
));
}
}Health Monitoring and Actuator
Configure health checks for proper Eureka integration:
# application.yml
management:
endpoints:
web:
exposure:
include: health,info,metrics
endpoint:
health:
show-details: always
health:
defaults:
enabled: true
eureka:
instance:
health-check-url-path: /actuator/health
status-page-url-path: /actuator/info@Component
public class CustomHealthIndicator implements HealthIndicator {
private final DataSource dataSource;
public CustomHealthIndicator(DataSource dataSource) {
this.dataSource = dataSource;
}
@Override
public Health health() {
try (Connection conn = dataSource.getConnection()) {
if (conn.isValid(1)) {
return Health.up()
.withDetail("database", "PostgreSQL")
.withDetail("status", "Connected")
.build();
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
return Health.down()
.withDetail("error", e.getMessage())
.build();
}
return Health.down().build();
}
}Discovery Client API
Use DiscoveryClient for programmatic service discovery:
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/discovery")
public class DiscoveryController {
private final DiscoveryClient discoveryClient;
public DiscoveryController(DiscoveryClient discoveryClient) {
this.discoveryClient = discoveryClient;
}
@GetMapping("/services")
public List<String> getServices() {
return discoveryClient.getServices();
}
@GetMapping("/services/{serviceId}/instances")
public List<ServiceInstanceInfo> getServiceInstances(@PathVariable String serviceId) {
return discoveryClient.getInstances(serviceId).stream()
.map(instance -> new ServiceInstanceInfo(
instance.getInstanceId(),
instance.getHost(),
instance.getPort(),
instance.isSecure(),
instance.getMetadata()
))
.toList();
}
}
public record ServiceInstanceInfo(
String instanceId,
String host,
int port,
boolean secure,
Map<String, String> metadata
) {}Common Mistakes to Avoid
Watch out for these common pitfalls when using Eureka:
1. Not Using Instance IDs for Multiple Instances
# Wrong - all instances have same ID
eureka:
instance:
instance-id: ${spring.application.name}
# Correct - unique ID per instance
eureka:
instance:
instance-id: ${spring.application.name}:${random.uuid}2. Missing @LoadBalanced Annotation
// Wrong - service name not resolved
@Bean
public RestTemplate restTemplate() {
return new RestTemplate();
}
// Correct - Eureka can resolve service names
@Bean
@LoadBalanced
public RestTemplate restTemplate() {
return new RestTemplate();
}3. Ignoring Self-Preservation Mode
# Development - disable self-preservation for faster eviction
eureka:
server:
enable-self-preservation: false
eviction-interval-timer-in-ms: 5000
# Production - keep self-preservation enabled
eureka:
server:
enable-self-preservation: true
renewal-percent-threshold: 0.854. Hardcoding Eureka URLs in Production
# Wrong - hardcoded URLs
eureka:
client:
service-url:
defaultZone: http://localhost:8761/eureka/
# Correct - externalized configuration
eureka:
client:
service-url:
defaultZone: ${EUREKA_SERVER_URL:http://localhost:8761/eureka/}Eureka vs Kubernetes Service Discovery
If you’re running on Kubernetes, built-in DNS-based discovery may replace Eureka:
| Feature | Eureka | Kubernetes |
|---|---|---|
| Setup | Requires Eureka server | Built-in |
| Client dependency | Spring Cloud Netflix | None (DNS) |
| Health checks | Heartbeats | Readiness probes |
| Load balancing | Client-side (Ribbon) | kube-proxy/Envoy |
| Best for | VM/Docker Compose | Kubernetes clusters |
Final Thoughts
Service discovery is fundamental for microservices, and Spring Cloud Eureka provides a battle-tested solution for Java applications. It eliminates hardcoded URLs, enables dynamic scaling, and integrates seamlessly with Spring Cloud Gateway and OpenFeign. For production deployments, run multiple Eureka servers for high availability and use proper health checks. If you’re moving to Kubernetes, evaluate whether Kubernetes-native service discovery meets your needs before adding Eureka.
To continue building your microservices architecture, read API Routing with Spring Cloud Gateway and Monitoring Microservices with Prometheus and Grafana. For official documentation, visit the Spring Cloud Netflix Reference and the Eureka Documentation.